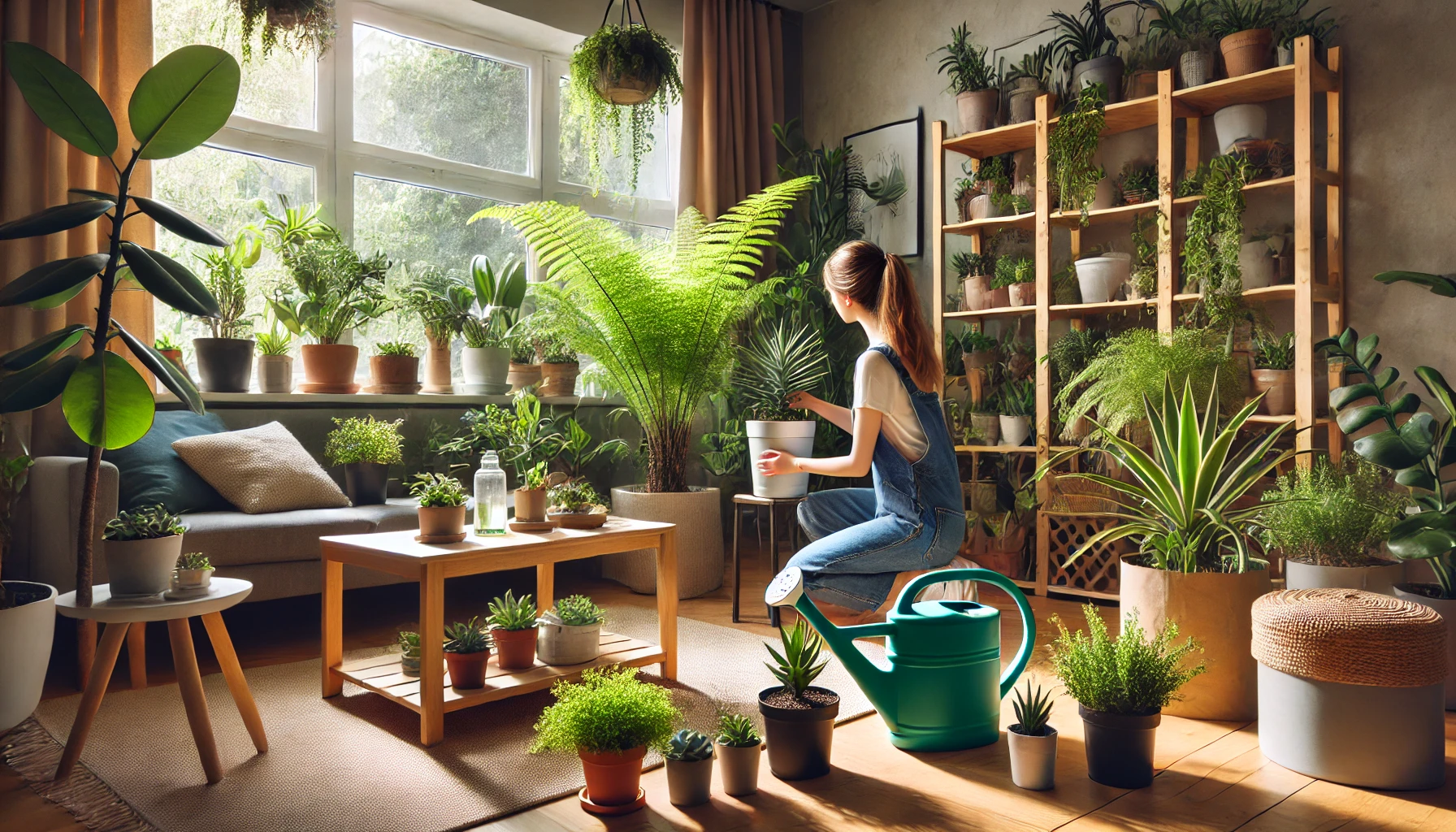
Fertilizing your indoor plants is essential for their health, growth, and vitality. While plants in nature receive nutrients from decomposing organic matter, those in indoor environments rely entirely on the care provided by their owner. Without proper fertilization, plants may struggle to thrive, showing signs of slow growth, pale leaves, or even poor blooming. This comprehensive guide will help you master the art of fertilizing indoor plants, ensuring they remain lush and healthy.
1. Why Fertilization is Important for Indoor Plants
Providing Fertilizers
Key nutrients found in fertilizers:
- Nitrogen (N): Encourages
- Phosphorus (P): Promotes
- Potassium (K): Strengthens
Why indoor plants need fertilizers:
- Limited nutrients in soil: Potting soil loses its nutrient content over time.
- No natural decomposition: Unlike outdoor environments, indoor plants do not benefit from the natural decomposition of organic matter.
- Restricted root systems: Plants in pots have limited space to grow.
2. Types of Fertilizers for Indoor Plants
Fertilizers come in various forms.
- Liquid Fertilizer:
- How it works: Provides a quick nutrient boost.
- Best for: Fast action, ideal for plants that need a quick nutrient increase.
- Slow-Release Fertilizer:
- How it works: Granules or pellets release nutrients gradually over time.
- Best for: Busy plant parents who prefer a low-maintenance approach.
- Organic Fertilizer:
- How it works: Derived from natural materials like compost, bone meal, or fish emulsion.
- Best for: Gardeners concerned with the environment and plants sensitive to synthetic chemicals.
- Synthetic Fertilizer:
- How it works: Made from chemical compounds, offering precise nutrient control.
- Best for: Plants with specific nutrient deficiencies.
- Foliar Fertilizer:
- How it works: Sprayed directly on leaves for absorption.
- Best for: Rapid nutrient uptake.
3. Signs Your Plants Need Fertilizer
Common indicators:
- Yellowing leaves: A sign of nitrogen deficiency.
- Slow growth: Indicates a lack of nutrients.
- Small or pale new leaves: May suggest phosphorus deficiency.
- Poor blooming: Lack of flowering could point to insufficient potassium.
- Leaf drop or weak stems: Could indicate a need for more nutrients.
By regularly observing your plants, you can determine when they need fertilization.
4. Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Plants
Different plants have different nutrient needs. Choosing a fertilizer suited to your plant’s needs ensures optimal growth and health.
Fertilizer recommendations by plant type:
- Plants with green foliage (e.g., Pothos, Monstera): Use a nitrogen-rich fertilizer for lush leaves.
- Flowering plants (e.g., peace lilies, anthuriums): Use a fertilizer with higher phosphorus content to support blooming.
- Succulents and cacti: Use a fertilizer with low nitrogen to prevent excessive leaf growth.
- Herbs (e.g., basil, mint): Use a balanced fertilizer to maintain stability.
- Ferns: Use a potassium-rich fertilizer to support their delicate nature.
Matching the right fertilizer to your plant ensures it receives the nutrients it needs without being overloaded.
5. How to Fertilize Indoor Plants Step by Step
Proper fertilization involves more than just applying fertilizer; timing, technique, and dosages are key.
Step-by-step fertilization guide:
- Read the label: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Water first: Ensure your plant is well-watered before fertilizing.
- Dilute the fertilizer: Use the recommended dilution rate to avoid over-fertilization.
- Apply evenly: Spread the fertilizer evenly around the plant.
- Avoid over-fertilizing: Excess nutrients can harm the plant.
Consistency and moderation are essential for effective fertilization.
6. Best Times to Fertilize Indoor Plants
The right time to apply fertilization ensures that your plants receive nutrients when they need them most.
When to fertilize:
- Growing season (spring and summer): Fertilize regularly to support active growth.
- Dormant season (fall and winter): Reduce or stop fertilization, as most plants grow more slowly during these months.
Exceptions: Some plants, like herbs or certain flowering species, may need light feeding during the dormant period.
Adjusting your schedule to your plant’s growth cycle is important for successful fertilization.
7. Avoiding Common Fertilization Mistakes
Even with the best intentions, mistakes can happen. Avoid these common fertilization errors:
- Over-fertilization:
- Symptoms: Brown tips on leaves or root burn.
- Solution: Flush the soil with water to remove excess fertilizer.
- Under-fertilization:
- Symptoms: Stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Solution: Gradually increase the amount of fertilizer.
- Using the wrong fertilizer:
- Symptoms: Poor growth or nutrient deficiencies despite fertilizing.
- Solution: Research your plant’s needs and switch to a more suitable formula.
8. Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers: Which is Better?
Both organic and synthetic fertilizers have pros and cons. Understanding their differences can help you decide which is best for your plants.
Organic Fertilizers:
- Pros:
- Environmentally friendly and improves soil health.
- Release nutrients slowly, reducing the risk of over-fertilization.
- Cons:
- Slower results compared to synthetic options.
- May have a stronger odor.
Synthetic Fertilizers:
- Pros:
- Provides precise nutrient control.
- Fast-acting for immediate results.
- Cons:
- May lead to salt buildup in the soil.
- Excessive use can harm the plant or the environment.
Choosing between organic and synthetic fertilizers depends on your priorities and the needs of your plants.
9. DIY Fertilizers for Indoor Plants
If you prefer natural and cost-effective options, homemade fertilizers can be an effective alternative.
Homemade fertilizer ideas:
- Banana peel water: Soak banana peels in water to create a potassium-rich solution.
- Coffee grounds: Lightly sprinkle on the soil to boost nitrogen.
- Eggshell powder: Crush eggshells and mix into the soil to add calcium.
- Compost tea: Brew compost in water to create a nutrient-rich liquid fertilizer.
Homemade solutions are sustainable and easy to customize.
10. Maintaining Healthy Soil After Fertilization
Fertilization is just one aspect of plant care. Maintaining healthy soil ensures nutrients are absorbed efficiently.
Tips for healthy soil:
- Aerate regularly: Loosen the top layer of soil to improve airflow.
- Flush periodically: Water the soil thoroughly to remove excess salts and prevent buildup.
- Repot as needed: Refresh the soil every 1-2 years to replenish nutrients and avoid compaction.
Healthy soil supports robust plant growth and minimizes the risk of nutrient imbalances.
Final Considerations: Feeding Your Plants for Success
Fertilizing indoor plants is both an art and a science that can dramatically improve their health and beauty. By understanding their unique needs, choosing the right fertilizers, and applying them properly, you can enjoy thriving greenery in any indoor space. With patience and care, your plants will reward you with vibrant foliage, strong roots, and stunning blooms.