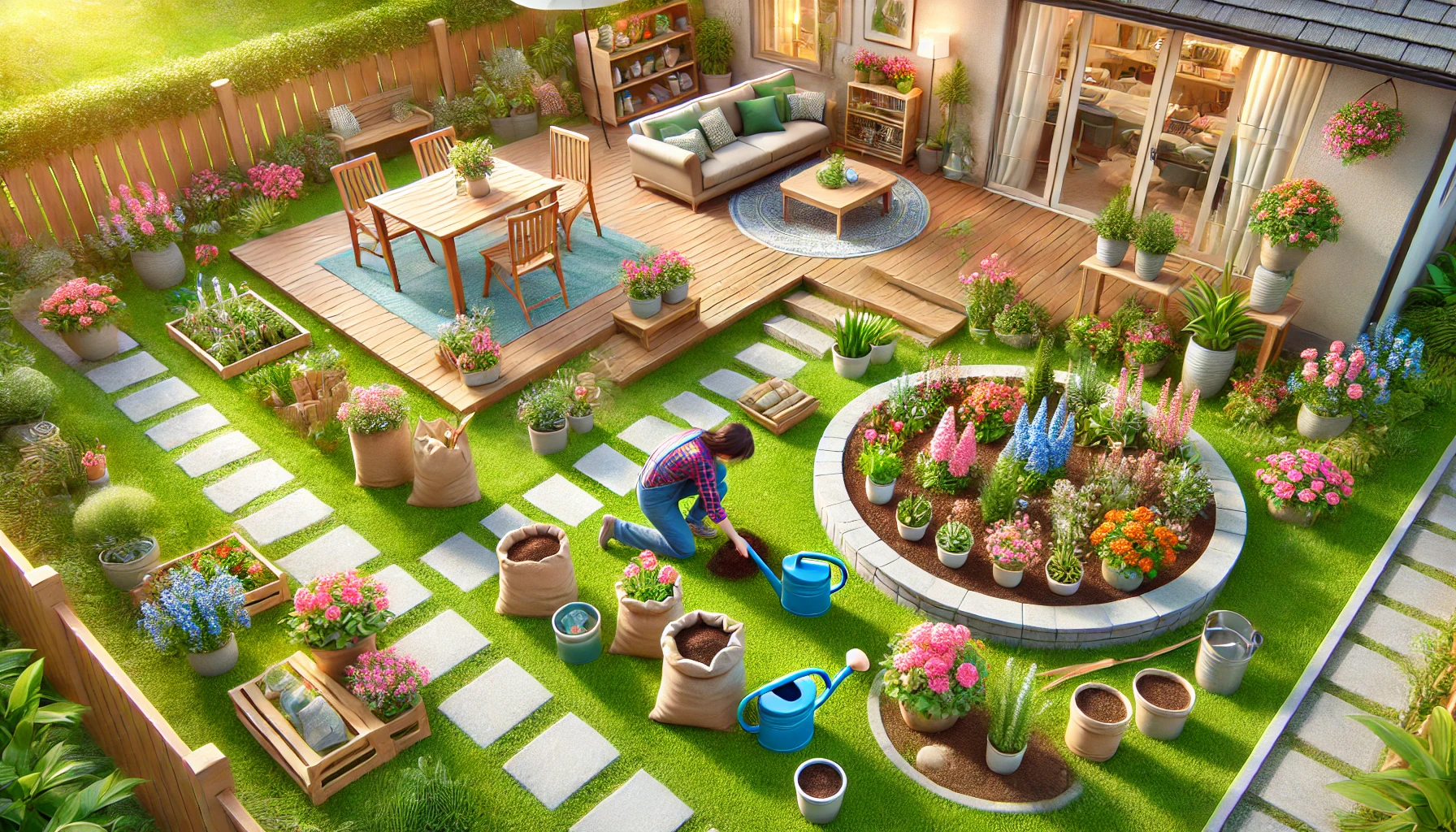
Creating a home garden from scratch is a rewarding experience that allows you to connect with nature, improve your outdoor space, and even grow your own food or flowers. While the process may seem overwhelming at first, careful planning and the right techniques will make it enjoyable and successful. Whether you have a small backyard or a large garden, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to start your home garden from scratch.
1. Planning Your Garden Space
Before you start planting, it’s essential to plan your garden space properly. This step will help you make the best use of your area and avoid common mistakes.
Measure Your Space
Begin by measuring your garden area. Whether you have a small balcony, a backyard, or a larger landscape, knowing the available space will help you determine what type of plants, layout, and structures you can incorporate.
Evaluate Sunlight and Shade
Observe how much sunlight different parts of your garden receive throughout the day. Some plants require full sun (at least 6 hours of direct sunlight), while others thrive in partial shade or full shade. This will influence where you place your plants.
Check Soil Quality
Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful garden. Perform a soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient content. If the soil lacks nutrients, you can enrich it with compost or organic matter to improve its fertility.
Decide on the Type of Garden
Consider what you want from your garden. Some popular options include:
- Flower Garden – Aesthetic and decorative
- Vegetable Garden – Fresh, homegrown food
- Herb Garden – Useful for cooking and medicinal purposes
- Mixed Garden – A combination of flowers, vegetables, and herbs
2. Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting the right plants ensures your garden thrives in your environment. Here are some factors to consider:
Climate and Hardiness Zone
Research which plants grow best in your climate. The USDA Hardiness Zone map (or equivalent in your country) will help you choose plants that can withstand local temperature variations.
Maintenance Level
If you are a beginner, start with low-maintenance plants like succulents, marigolds, lavender, or native plants that require less care.
Companion Planting
Some plants grow better together. For example, basil and tomatoes support each other’s growth, while marigolds help repel pests from vegetables.
3. Preparing the Soil
Good soil is crucial for plant health. Here’s how to prepare your garden bed:
Clear the Area
Remove weeds, rocks, and debris from your garden space. This creates a clean slate for planting.
Loosen the Soil
Use a shovel or garden fork to turn and aerate the soil. This improves drainage and allows plant roots to spread more easily.
Enrich with Organic Matter
Add compost, aged manure, or organic fertilizer to increase soil fertility. If your soil is too sandy or too clay-heavy, amend it with materials like peat moss or compost to balance moisture retention and drainage.
4. Designing Your Garden Layout
A well-thought-out design enhances both the beauty and functionality of your garden. Consider the following:
Create Pathways
Use stepping stones, gravel, or wood chips to create walkways. This helps prevent soil compaction and makes maintenance easier.
Plan Plant Placement
- Place taller plants at the back of garden beds.
- Arrange shorter plants in front for better visibility.
- Keep plants with similar water and sunlight needs together.
Use Raised Beds or Containers
If you have limited space or poor soil quality, consider raised garden beds or container gardening. These options provide better control over soil conditions and drainage.
5. Planting Your Garden
Now that your soil and layout are ready, it’s time to plant. Follow these steps for successful planting:
Dig Proper Holes
Each plant has different spacing and depth requirements. Follow the instructions on seed packets or plant labels.
Water Before Planting
Water the soil before planting to prevent transplant shock and help roots establish more easily.
Apply Mulch
Mulching helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use organic mulch like wood chips, straw, or shredded leaves.
6. Watering and Garden Maintenance
Keeping your garden well-maintained is essential for healthy plant growth.
Watering Tips
- Water deeply and less frequently to encourage strong root growth.
- Morning watering is best to prevent evaporation and fungal diseases.
- Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to ensure efficient watering.
Weed Control
Weeds compete with plants for nutrients and water. Remove them regularly by hand or use mulch to minimize their growth.
Pruning and Deadheading
- Prune shrubs and perennials to maintain shape and promote new growth.
- Deadhead flowers (remove spent blooms) to encourage continuous blooming.
Fertilization
Feed your plants with organic or slow-release fertilizers to provide necessary nutrients. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can harm plant roots.
7. Protecting Your Garden from Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases can damage your plants if not controlled early.
Preventive Measures
- Rotate crops each season to prevent soil-borne diseases.
- Space plants properly to improve air circulation and reduce fungal infections.
- Keep your garden clean by removing dead leaves and plants.
Natural Pest Control
- Encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs and bees that help control pests.
- Use neem oil, garlic spray, or insecticidal soap to deter unwanted insects.
- Introduce companion plants like marigolds, which repel aphids and nematodes.
8. Adding Personal Touches to Your Garden
Make your garden a relaxing and enjoyable space by adding unique elements:
DIY Garden Decorations
- Paint flower pots with creative designs.
- Add garden markers for herbs and vegetables.
Seating and Relaxation Areas
- Place a bench, swing, or hammock to create a peaceful retreat.
- Add an outdoor dining area for garden meals.
Garden Lighting
- Install solar-powered lights along pathways.
- Use string lights for a warm ambiance at night.
9. Seasonal Garden Care
Each season requires different care for your garden:
Spring
- Plant new flowers and vegetables.
- Apply fresh mulch and compost.
Summer
- Increase watering during hot days.
- Remove faded flowers and overgrown plants.
Autumn
- Plant perennials and bulbs for the next season.
- Rake leaves and prepare for winter.
Winter
- Protect delicate plants with covers.
- Plan next year’s garden layout and improvements.
Conclusion: Enjoy the Beauty of Your Garden
Creating a home garden from scratch requires time and patience, but the results are incredibly rewarding. By planning your space, selecting the right plants, and maintaining your garden with care, you can enjoy a thriving, beautiful outdoor space. Gardening is a lifelong journey of learning and experimentation, so don’t be afraid to try new ideas and techniques.
Now, step outside, get your hands in the soil, and start creating your dream garden! 🌿🌻✨