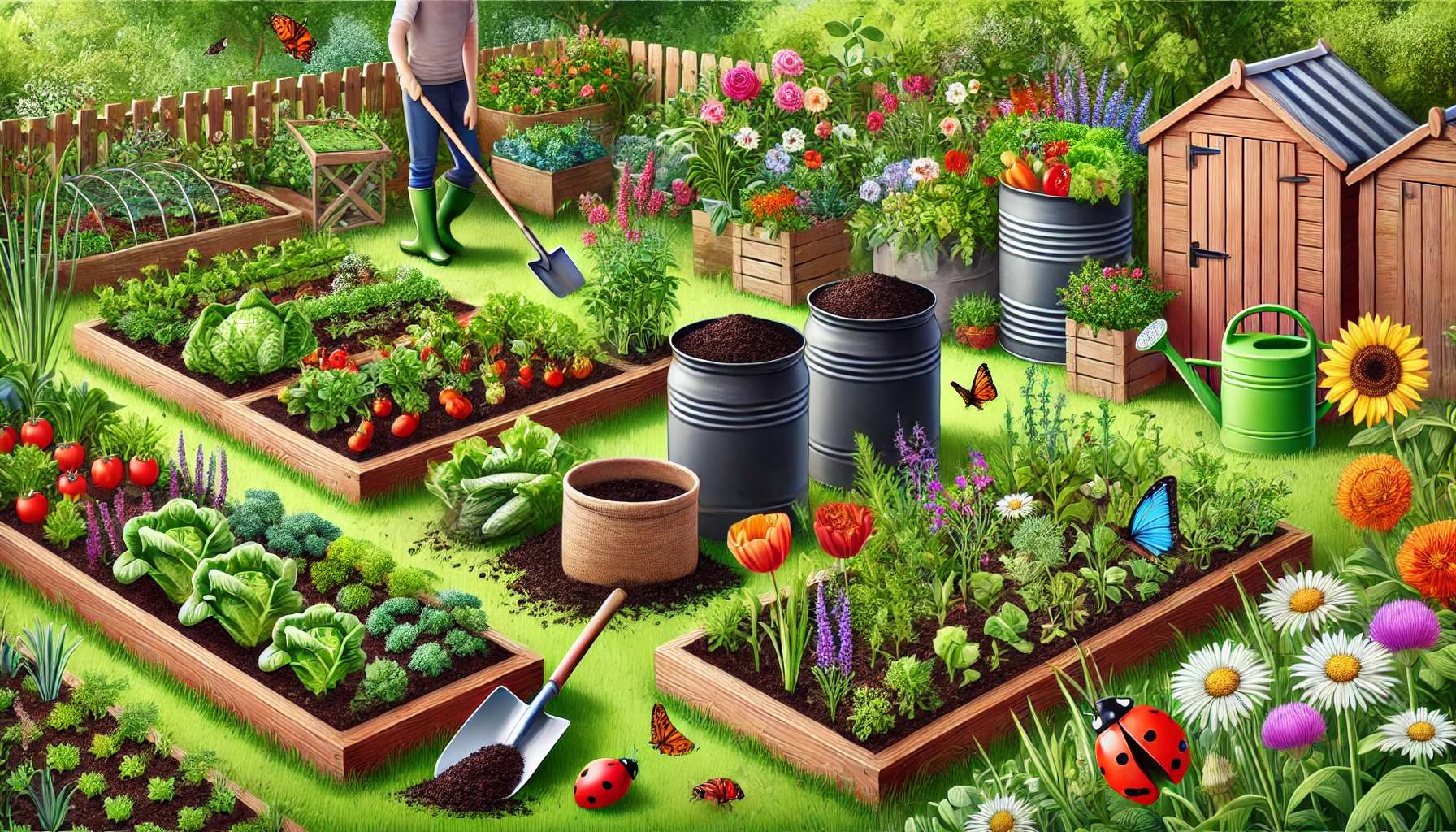
Organic gardening is a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to grow healthy plants without relying on synthetic chemicals. By using natural fertilizers, compost, and eco-friendly pest control methods, you can cultivate a thriving garden that benefits both your plants and the environment. Whether you’re growing vegetables, herbs, flowers, or fruit trees, adopting organic gardening techniques will improve soil health, promote biodiversity, and produce safer, chemical-free food.
In this guide, you’ll learn the best organic gardening practices, including soil management, composting, natural pest control, and eco-friendly watering techniques to help your garden flourish.
1. Building Healthy Soil for Strong Plants
The foundation of a thriving organic garden starts with healthy soil. Nutrient-rich soil supports plant growth, improves water retention, and prevents diseases.
A. Understanding Soil Composition
Healthy soil consists of a balance of sand, silt, clay, organic matter, and microorganisms. Testing your soil’s pH and nutrient levels helps determine what amendments are needed.
B. Enriching Soil Naturally
- Compost: Improves soil structure, increases fertility, and enhances microbial activity.
- Aged Manure: Provides slow-release nutrients but must be well-composted to avoid burning plants.
- Cover Crops (Green Manure): Plants like clover, alfalfa, or rye add organic matter and improve soil health when tilled into the ground.
- Mulching: A layer of organic mulch (straw, leaves, or wood chips) protects the soil, conserves moisture, and suppresses weeds.
✅ Tip: Avoid synthetic fertilizers, as they can disrupt soil microbiology. Instead, use organic amendments like compost tea, worm castings, or fish emulsion to feed your plants naturally.
2. Composting: Turning Waste into Nutrients
Composting is an essential practice in organic gardening. It reduces kitchen and garden waste while creating a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
A. What to Compost?
✔ Greens (Nitrogen-Rich): Vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings.
✔ Browns (Carbon-Rich): Dry leaves, straw, shredded cardboard.
✔ Water & Air: Keep the pile moist and aerated to speed up decomposition.
B. What to Avoid?
❌ Meat, dairy, or oily foods (they attract pests).
❌ Diseased plants or weed seeds (can spread diseases or unwanted growth).
C. How to Maintain a Compost Pile?
- Turn the compost every 1-2 weeks to accelerate decomposition.
- Keep it moist but not soggy (like a wrung-out sponge).
- Add a mix of greens and browns to maintain balance.
✅ Tip: Finished compost is dark, crumbly, and has an earthy smell. Use it in garden beds, pots, or as a top dressing for plants.
3. Natural Pest and Disease Control
Pests and plant diseases can be controlled without harmful chemicals by using natural methods that maintain garden balance.
A. Companion Planting to Repel Pests
Certain plants naturally deter harmful insects and benefit each other when grown together.
✔ Basil & Tomatoes: Basil repels aphids and enhances tomato flavor.
✔ Marigolds & Vegetables: Marigolds deter nematodes and aphids.
✔ Lavender & Roses: Lavender repels moths and improves garden aesthetics.
B. Encouraging Beneficial Insects
Not all bugs are bad! Many help control pests naturally.
✔ Ladybugs: Eat aphids and mites.
✔ Praying Mantises: Consume a variety of harmful insects.
✔ Bees & Butterflies: Pollinate flowers and vegetables.
C. Organic Pest Control Remedies
If pest problems persist, try these chemical-free solutions:
- Neem Oil Spray: Effective against aphids, mites, and whiteflies.
- Garlic & Chili Spray: Repels chewing insects.
- Diatomaceous Earth: A natural powder that dehydrates soft-bodied pests.
✅ Tip: Keep your garden diverse and full of life to maintain a balanced ecosystem that naturally controls pests.
4. Watering the Organic Way
Efficient watering helps conserve resources while keeping plants healthy. Overwatering or watering at the wrong time can lead to root rot, fungal diseases, and nutrient loss.
A. Best Time to Water
- Early Morning: Prevents evaporation and allows plants to absorb moisture.
- Late Afternoon: Can work, but avoid wetting foliage overnight (to prevent fungal growth).
B. Watering Methods for Organic Gardens
✔ Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the roots, reducing waste.
✔ Soaker Hoses: Slowly release water along the soil surface.
✔ Mulching: Reduces evaporation and maintains consistent soil moisture.
C. Collecting Rainwater for Sustainability
Rainwater harvesting is a great way to reduce dependency on tap water.
✔ Install a rain barrel to collect water from rooftops.
✔ Use collected rainwater for watering plants and reducing costs.
✅ Tip: Avoid overwatering—most plants prefer deep, infrequent watering over shallow, daily watering.
5. Organic Fertilization for Long-Term Soil Health
Instead of synthetic fertilizers, organic gardening relies on natural fertilizers that feed the soil while improving its long-term fertility.
A. Best Organic Fertilizers
✔ Compost Tea: A liquid fertilizer made by steeping compost in water.
✔ Banana Peels: Rich in potassium, ideal for flowering plants.
✔ Epsom Salt: Provides magnesium to strengthen plant growth.
✔ Worm Castings: Improve soil structure and add beneficial microbes.
B. Crop Rotation to Prevent Nutrient Depletion
Rotating crops prevents soil exhaustion and reduces pest buildup.
- Year 1: Plant nitrogen-heavy crops (tomatoes, spinach).
- Year 2: Follow with legumes (beans, peas) to replenish nitrogen.
- Year 3: Grow root vegetables (carrots, onions) to improve soil texture.
✅ Tip: Avoid planting the same crop in the same spot for consecutive years to prevent nutrient depletion.
6. Sustainable Weed Management
Weeds compete with plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Instead of chemical herbicides, use organic weed control methods.
✔ Hand Pulling & Hoeing: Best for small gardens, especially after rain.
✔ Mulching: Suppresses weed growth by blocking sunlight.
✔ Boiling Water or Vinegar: Kills weeds naturally (but avoid nearby plants).
✅ Tip: A thick layer of organic mulch (like wood chips or straw) reduces the need for weeding and improves soil health.
7. Encouraging Biodiversity in Your Garden
A diverse garden attracts beneficial insects, improves soil health, and supports pollinators.
✔ Plant a mix of flowers, vegetables, and herbs to create a balanced ecosystem.
✔ Include flowering plants that provide nectar for bees and butterflies.
✔ Grow native plants that thrive in your climate with minimal care.
✅ Tip: Creating a pollinator-friendly space with native plants ensures a thriving, self-sustaining garden.
Final Thoughts
Organic gardening is more than just avoiding synthetic chemicals—it’s about working with nature to create a healthier, more sustainable garden. By building fertile soil, using natural pest control, conserving water, and maintaining biodiversity, you’ll grow strong, resilient plants while protecting the environment.
🌿 Now it’s time to start your organic garden! Whether you’re growing vegetables, herbs, or flowers, these eco-friendly practices will help you cultivate a lush and productive space naturally.